Go is a compiled programming language designed by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson at google.
It is statically typed language which is syntactically similar to C language but offering additional features like structural typing, garbage collection, memory safety, and CSP-style concurrency.
Diving deep into the GO debugger tool: Delve
Using Delve, you can view, add and change breakpoints in a Go program, navigate the program either line-wise or through breakpoints, inspect variables, functions, and expression values, and finally analyze all the programs in details.
Let us first install the Delve debugger tool.
Downloading and installing Go Delve
Go Delve can be downloaded and installed by using the go get command.
Linux, Windows, OSX
Clone the git repository and build:
Alternatively, on Go version 1.16 or later:
The following elements should already be set up if you have a working Go installation:
- · Make sure GOBIN env variable is properly set, which will indicate the directory where the dlv (Delve) command will be stored. You can check by typing :
-> go env GOBIN
- Make sure PATH contains GOBIN which will allow you to run Go binary executables without specifying the absolute path
You can view all the environment variables of your GO environment using the “go env” command. You can run the go env command on the command prompt, the following will the output.
- The next step is to set the GOBIN path, you can use the following command:
- Copy the path as shown in the below picture and add it to the environment variable.
- You’ll be able to run the “dlv” command in the terminal.
- In order to start the debug mode, run the following command from your directory: “dlv debug”
- A test environment will be displayed for debugging. You can check the commands for dlv by typing the help command.
You have finally set up our environment, and now you are ready to debug the code !!
Following is the code that we will be using for debugging:
- Following are the steps for using Delve debugging tool:
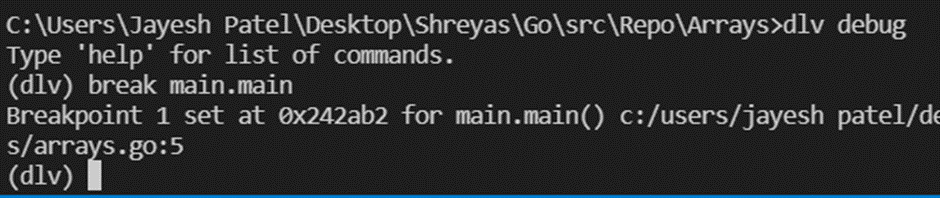
- Initially, we’ll put the breakpoint in the main function using the “break main. main” command.
2. Let’s put a break at lines 8, 12, and 25.
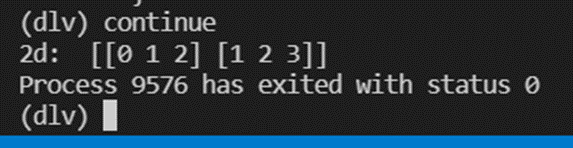
3. Type “continue” to see break points in the code in debugging mode.
4.As shown in the above image, you can see there is a breakpoint at the main function.
5. Type “continue” again to see the next breakpoint and type “locals” for viewing local variables declared in the line.
6. If you visit breakpoint at line 12 after typing “continue”, you’ll be able to see the output of above code line 12.
7. After continuing the last line i.e. line 25, you’ll be able to see the following output which states “Process 9576 has exited with status 0” if there is no error in your code.
8.To exit from the test environment type the exit command.
You have finally debugged the code using delve …. 👍
For any further Queries or anything related to Golang Development,Coding, Blogging, Tech Documentation you can DM me on Linkedin or instagram id=acanubhav94.
Start blogging about your favorite technologies, reach more readers and earn rewards!
Join other developers and claim your FAUN account now!

anubhav chaturvedi
Freelancer
@aniforverizonUser Popularity
37
Influence
4k
Total Hits
1
Posts


























Only registered users can post comments. Please, login or signup.