CDNs are collections of geographically distributed caches that place content closer to end-users to improve performance and reduce traffic on backbone networks. Placing CDN caches inside ISPs networks - embedded caches - has become increasingly popular, but it also adds complexity to operating caches managed by other networks inside the borders.
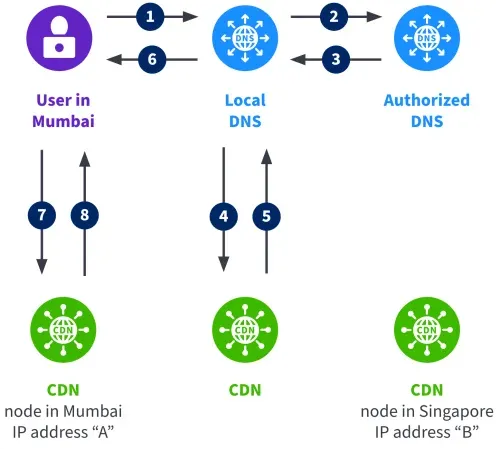
CDNs use different methods to map end-users to caches, such as BGP , DNS server mapping, and anycast.
According to the author, ISPs should consider regionalizing IP addresses and deploying caches strategically to reduce traffic on the network edge.
Give a Pawfive to this post!
Start writing about what excites you in tech — connect with developers, grow your voice, and get rewarded.
Join other developers and claim your FAUN.dev() account now!















