Google API Keys Weren't Secrets. But then Gemini Changed the Rules
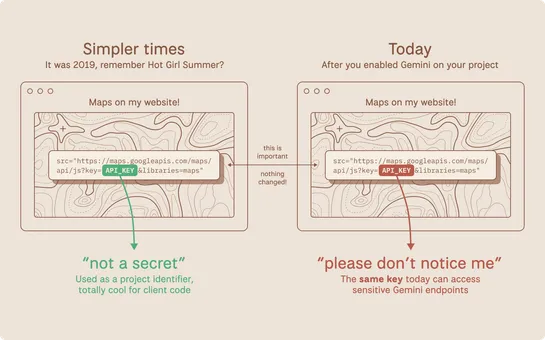
A report reveals Google Cloud'sAPI keysuse the same format for public IDs and secret auth. That overlap lets public keys reach theGemini API. New keys default toUnrestricted. Existing keys can be retroactively granted Gemini access. Google will add scoped defaults, block leaked keys, and notify affe.. read more