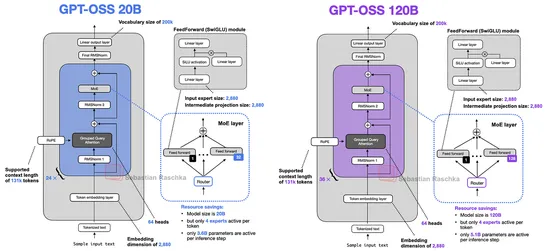
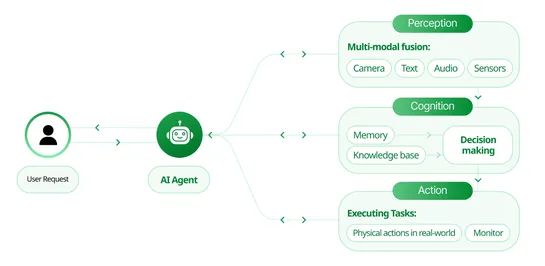
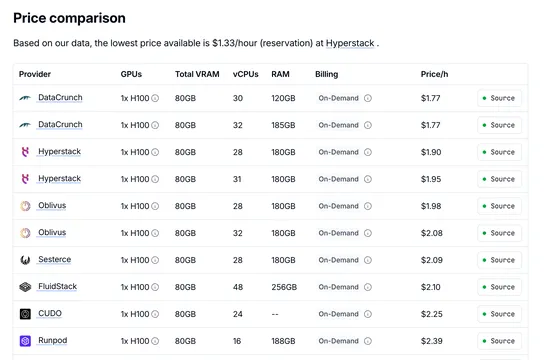
From GPT-2 to gpt-oss: Analyzing the Architectural Advances
OpenAI Returns to Openness. The company droppedgpt-oss-20Bandgpt-oss-120B—its first open-weight LLMs since GPT-2. The models pack a modern stack:Mixture-of-Experts,Grouped Query Attention,Sliding Window Attention, andSwiGLU. They're also lean. Thanks toMXFP4 quantization, 20B runs on a 16GB consume..