Microservices Observability in a Kubernetes World: Logs
Setting Up Loki for Log Aggregation
Loki is a horizontally scalable, highly available, multi-tenant log aggregation system inspired by Prometheus. Think of it as "Prometheus for logs." It is built to be cost-efficient and simple to operate. Instead of indexing the full contents of logs, Loki indexes only a set of labels for each log stream, which makes it lightweight and efficient. It integrates easily with Promtail and Grafana since it was designed for that purpose.
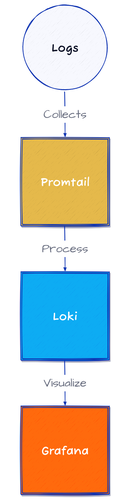
Together, these 3 components form a complete logging stack:
- Promtail: Collects logs from Kubernetes and sends them to Loki.
- Loki: Stores logs and allows users to query them.
- Grafana: Displays logs from Loki in a natively accessible way.
The integration process is straightforward.
Loki logging stack
To begin, we'll install the Loki data source plugin using Helm with a custom configuration.
Follow these steps:
- Create a working directory and navigate to it.
cd $HOME/monitoring
mkdir loki && cd loki
Add the Loki Helm repository:
helm repo add grafana \
https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
Create a values.yaml file with the following content:
cat < values.yaml
deploymentMode: SingleBinary
loki:
auth_enabled: false
commonConfig:
replication_factor: 1 # Replication factor for Loki data
# 1 means no replication => single server
limits_config:
allow_structured_metadata: false # Disable structured metadata for compatibility
# with schema v11 and boltdb-shipper
storage:
type: 'filesystem'
schemaConfig:
configs:
# Storage schema configuration - defines how Loki organizes and stores data
- from: 2020-10-24 # Start date for applying this schema (YYYY-MM-DD)
# All logs from this date onward use this schema
store: boltdb-shipper # Database type for indexes (log metadata)
# boltdb-shipper: simple local database, ideal for beginners
object_store: filesystem # Storage type for chunks (actual log data)
# filesystem: stores data on the local file system
schema: v11 # Loki schema version to use
# v11–v13: recommended versions for new installations
index:
prefix: index_ # Prefix added to index file names
# Helps organize files in storage
period: 24h # Duration of each index period (24 hours)
# A new index is created every 24h to optimize performance
# Using the "SingleBinary" or monolithic deployment mode
singleBinary:
replicas: 1
resources: # Resource limits for the Loki container
requests: # Minimum guaranteed resources
cpu: 100m # 100 millicores = 0.1 CPU
memory: 128Mi # 128 MiB of minimum RAM
limits: # Maximum allowed resources
cpu: 500m # 500 millicores = 0.5 CPU
memoryCloud-Native Microservices With Kubernetes - 2nd Edition
A Comprehensive Guide to Building, Scaling, Deploying, Observing, and Managing Highly-Available Microservices in KubernetesEnroll now to unlock all content and receive all future updates for free.