Understanding How Rancher Imports Clusters
Centralizing the management of all your clusters in Rancher is one of the key benefits of using the platform. In addition to creating new clusters, Rancher can also import existing clusters. For example, you may already have a Kubernetes cluster running on a cloud-managed service (like DOKS, EKS, GKE, or another cloud provider) or a self-managed cluster (like RKE, K3s, or another Kubernetes distribution) and you want to manage it using Rancher. You can simply import it and manage it from the UI.
ℹ️ You should not import a cluster that has already been connected to another instance of Rancher as it will lead to data corruption.
To import a cluster, you need to follow these steps:
- Go to
GLOBAL APPS>Cluster Management. - Click on
Import Existing.
At this step, you should see different providers including EKS, AKS, and GKE. If your cluster is not on one of these providers, you can use the Generic option. This is our case since we are using RKE2.
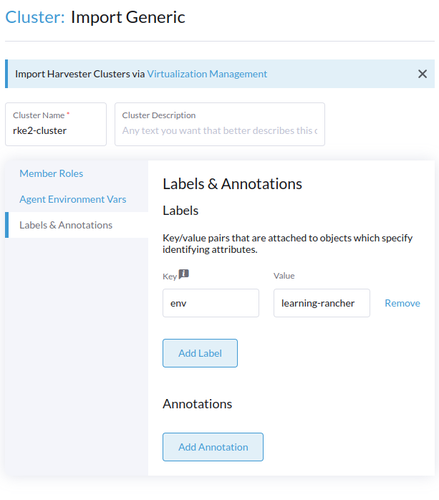
You can provide a name and labels to your cluster to help you identify it later:
- In the
Cluster Namefield, provide a name for your cluster. We will userke2-cluster. - In the
Labels & Annotationssection, add the label:env: learning-rancher. - In the
Agent Environment Variablessection, you should add the following environment variable to avoid certificate issues during the import process:STRICT_VERIFY:false
Here is a table to summarize the configurations:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Cluster Name | rke2-cluster |
| Labels & Annotations | env: learning-rancher |
| Environment Variables | STRICT_VERIFY: false |
Importing a cluster in Rancher
- Click on
Create.
End-to-End Kubernetes with Rancher, RKE2, K3s, Fleet, Longhorn, and NeuVector
The full journey from nothing to productionEnroll now to unlock all content and receive all future updates for free.