Lee Robinson, VP of Developer Experience at Vercel, provides an overview of databases that are well-suited for use with modern application and compute providers, such as serverless and edge compute.
The author focuses on transactional workloads, and evaluates databases based on the following criteria: compatibility with serverless and edge compute, compatibility with JavaScript and TypeScript codebases, being connectionless, web-native, lightweight, and type-safe.
They also discuss the new programming model that has emerged in response to the requirements of serverless and edge compute, as well as the current trends in the backend space.
Here is a list of the 1500 most common and useful solutions for data structure and algorithm programs, which are often asked in interviews and programming practices.
The blog post discusses the use of the python-gitlab library to interact with the GitLab API.
It covers basic usage of the library, such as working with API objects, attributes, pagination, and resultsets. The post then moves on to advanced DevSecOps use cases for API read and write actions, such as checking project settings, creating issue indexes, and optimizing code performance. Finally, the post provides tips for advanced custom configuration and CI/CD integration, as well as suggestions for further use cases.
The coolest open-source software tools in 2022 include the Apache Druid database, Apache Iceberg data analytics tool, Grafana observability software and TensorFlow machine learning platform.
OpenAI is expanding its AI capabilities by hiring hundreds of international contractors to teach its AI software engineering. The company aims to advance its Codex technology, which converts natural language into code, potentially replacing some human coders.
OpenAI's contractors are tasked with finding bugs in AI code and providing explanations for fixing them. This training data will be fed into OpenAI's AI technology. ChatGPT, owned by OpenAI, already threatens to disrupt several industries and might add software engineering to its list.
Infrastructure-from-Code (IfC) is a new way of thinking about cloud infrastructure that seeks to derive infrastructure from the application code, rather than defining it as code. This process analyzes the application code to infer the cloud resources needed and creates and maintains them without manual configuration.
There are two main approaches to IfC, with language-based tools introducing new programming languages and SDK-based tools introducing their own SDKs. Both aim to make it easier for developers to provision and tear off infrastructure, unlocking a generational leap in productivity.
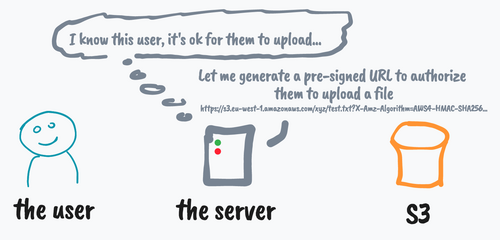
S3 pre-signed URLs provide a way for various clients to upload and download files in a controlled manner from Amazon S3. By default, all objects in S3 are private and require proper credentials or the AWS SDK to add new objects or retrieve the content of an object.
Pre-signed URLs are specially crafted S3 URLs with embedded credentials and time-limited availability, generated by the server using its own credentials. The user can make an HTTP request (PUT or POST) to the pre-signed URL to upload or download the object, without having to know anything about S3 or the AWS authentication protocols.
Pre-signed URLs can be used in various use cases such as uploading photos, downloads of large files, document management, marketing campaigns, and inter-system communication.
More details and most importantly illustrations are available in this article.