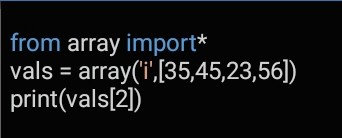
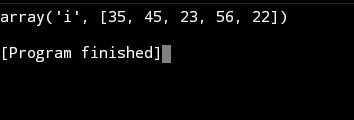
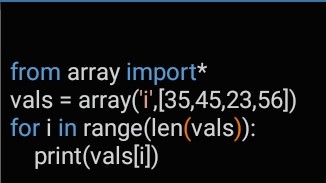
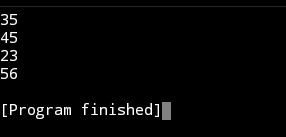
Introduction
By a collection of similar data types I mean if we want to store whole numbers/integers we can have our array that only contains integer elements, the same applies for strings, floats, and other data types.
Let’s say we have x = 100, this means we have declared variable x with a value of 100 in memory.
Memory is made up of bytes, one byte is 8 bits so we can describe memory as a long tape of bytes.
When we run x = 100, the memory manager allocates 4 bytes in memory, integer elements are usually allocated 4 bytes.
Remember 1 byte is 8 bits, so 4 bytes is 4*8 which is 32 bits, our integer 100 is converted into binary (10101110) as 29 zeros and then 101.
00000000
0000000)
00000000
00000101
The binary number is stored in memory, the 4 bytes are allocated 4 spaces in memory with 8 bits to each section.
Now if we wanted to store 10 student values, we would need 10 variables: