Scaling PostgreSQL to power 800 million ChatGPT users
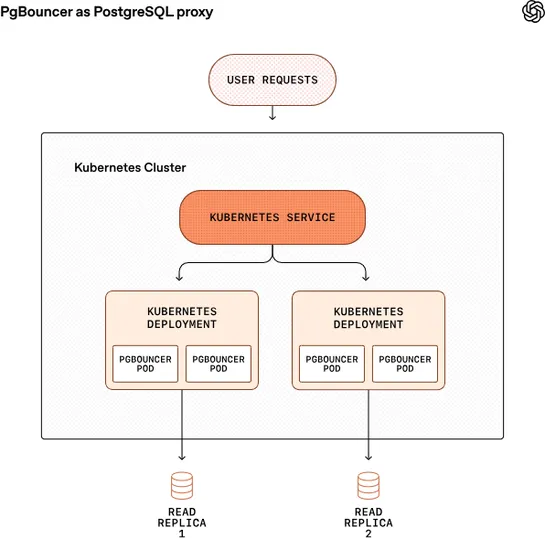
OpenAI pushedPostgreSQLto handle millions of QPS across 800M users. How? Nearly 50 read replicas, heavy read offloading, and serious trimming on write pressure. Writes? Sent elsewhere. Sharded systems likeCosmosDB, lazy writes, and app-level tweaks helped sidestep PostgreSQL’sMVCCwrite amplification.. read more